When qualifying a transformer bushing for its seismic performance there are two industry standards that can be used; IEEE 693-2005 Annex D and IEC TS 61463. IEEE 693-2005 is the recognized industry standard worldwide and is generally the one selected to qualify equipment. When comparing the two standards (IEEE vs IEC Comparison Table) it can be concluded that the IEEE 693-2005 Annex D High Performance time history shake table testing is the more stringent test for qualifying transformer bushings. This is based on:
- 2% damping is used by IEEE for the test versus 5% damping used by IEC.
- A vertical acceleration equal to 80% of the horizontal is used by IEEE versus a vertical acceleration equal to 50% of the horizontal used by IEC.
- IEEE requires that the bushing be mounted on a rigid stand and the bushing tested to twice the input level required at the top of the bushing. This means that the bushing gets tested to 4 times its high performance RRS or 2.0g ZPA. IEC uses a super-elevation factor of 1.5 or 2.0 to calculate the acceleration value of the bushing flange. This results in a less severe test ZPA.
In 2015 two 230 kV RIF® bushings were seismically qualified by shake table testing according to IEEE 693-2005. This testing was performed at the Structural Engineering & Earthquake Simulation Laboratory (SEESL) at the University of Buffalo. The test samples were two identical 230 kV RIF® bushings. The test bushings were mounted 13° from vertical on a rigid adaptor securely affixed to the shake table (see Figure 1). A 7 kg load in accordance with the requirements of IEEE 693 was placed at the top terminal connection of the test bushings. One bushing was tested for the normal IEEE 693-2005 High Performance Level. To cover a possible future IEEE 693 requirement the second bushing was tested with an extended plateau (15.5 Hz) for the High Performance Level.

Figure 1 - Test Configuration
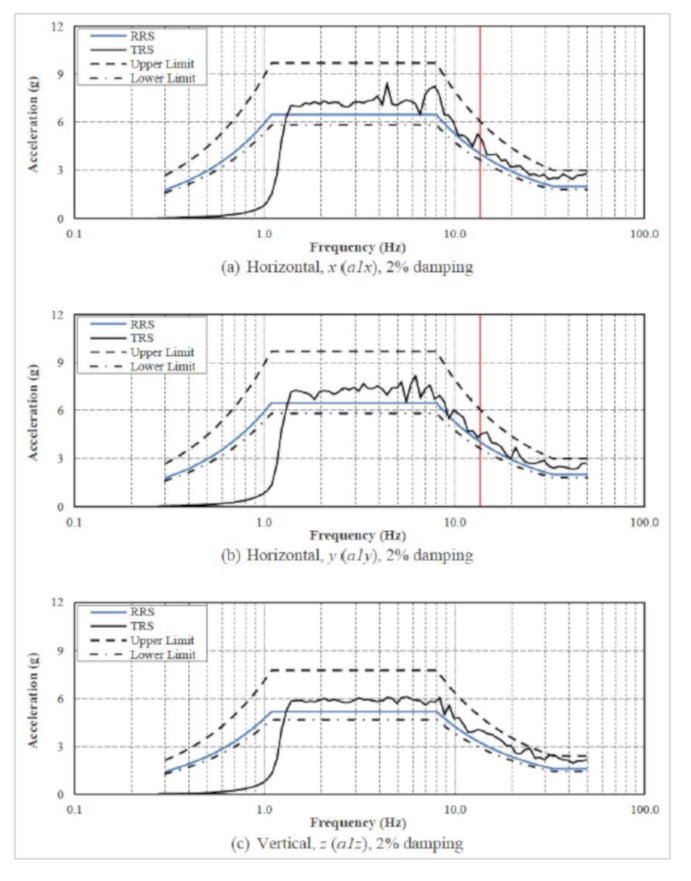
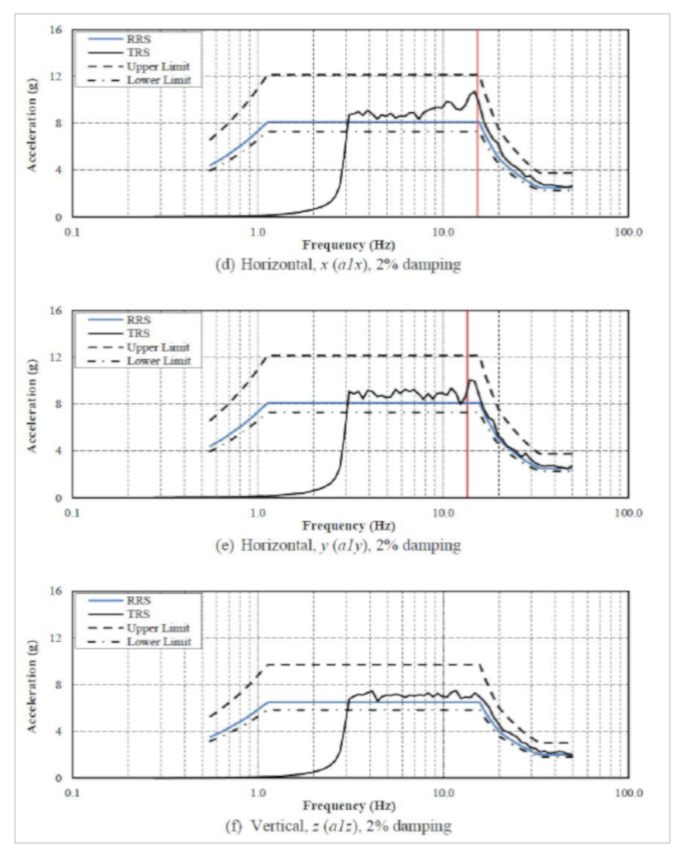
The following plots extracted from the certified test report show the recorded test response spectrum (TRS) compared with the required response spectrum (RRS) in 3 principal directions (X, Y and Z) for the High Performance 2.0g ZPA test and the High Performance 2.5g ZPA extended plateau test. Both test bushings qualified for their respective High Performance Levels.